Kö-Bogen II Office Building

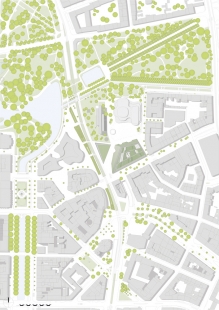
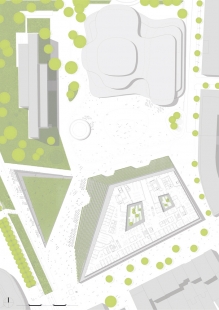
Sustainability is a mission: Eight kilometers of hornbeam hedges for a supergreen®-project. Over 30,000 plants – Europe’s largest green facade. The facade is an essential element of the Kö-Bogen II commercial and office building. The ensemble marks the conclusion of an urban renewal project in the heart of Düsseldorf. It also represents a paradigm shift: from an urban perspective, it signals a departure from the automotive era and a turn towards people-oriented planning. With Europe’s largest green facade, it offers an urban response to climate change and creating a new green heart in Düsseldorf’s inner city.
Today, where an elevated motorway once dominated the landscape, the Hofgarten has moved back into the heart of the city. Kö-Bogen’s sloping green facades face one another in a composition inspired by Land Art. The new building complex oscillates in a deliberate indeterminacy between city and park. The two structures form a dynamic entrance to Gustaf-Gründgens-Platz, which opens up the view to icons of post-war modernism – the clear austerity of the Dreischeibenhaus (1960) and the buoyant lightness of the Schauspielhaus (1970). Kö-Bogen II is a contemporary response to these two historic landmarks, without competing with them.
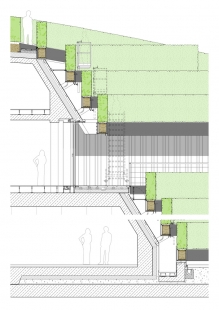
Going green. The hornbeam was intentionally selected as a native hardwood species that keeps its leaves in winter. A comprehensive phytotechnological concept was developed together with Prof. Dr. Strauch, Beuth University of Applied Sciences, Berlin, to incorporate the hedges into the building design. The greenery improves the city’s microclimate – it protects against the sun’s rays in summer and reduces urban heat, binds carbon dioxide, stores moisture, attenuates noise, and supports biodiversity.
The ecological benefit of the hornbeam hedges is equivalent to that of approximately 80 fully grown deciduous trees. This integration of nature into architecture offers a contemporary urban response to climate change. The aim of Kö-Bogen II is to pursue an overall ecological concept, explicitly to improve the city's microclimate.
Today, where an elevated motorway once dominated the landscape, the Hofgarten has moved back into the heart of the city. Kö-Bogen’s sloping green facades face one another in a composition inspired by Land Art. The new building complex oscillates in a deliberate indeterminacy between city and park. The two structures form a dynamic entrance to Gustaf-Gründgens-Platz, which opens up the view to icons of post-war modernism – the clear austerity of the Dreischeibenhaus (1960) and the buoyant lightness of the Schauspielhaus (1970). Kö-Bogen II is a contemporary response to these two historic landmarks, without competing with them.
Going green. The hornbeam was intentionally selected as a native hardwood species that keeps its leaves in winter. A comprehensive phytotechnological concept was developed together with Prof. Dr. Strauch, Beuth University of Applied Sciences, Berlin, to incorporate the hedges into the building design. The greenery improves the city’s microclimate – it protects against the sun’s rays in summer and reduces urban heat, binds carbon dioxide, stores moisture, attenuates noise, and supports biodiversity.
The ecological benefit of the hornbeam hedges is equivalent to that of approximately 80 fully grown deciduous trees. This integration of nature into architecture offers a contemporary urban response to climate change. The aim of Kö-Bogen II is to pursue an overall ecological concept, explicitly to improve the city's microclimate.
ingenhoven architects
0 comments
add comment